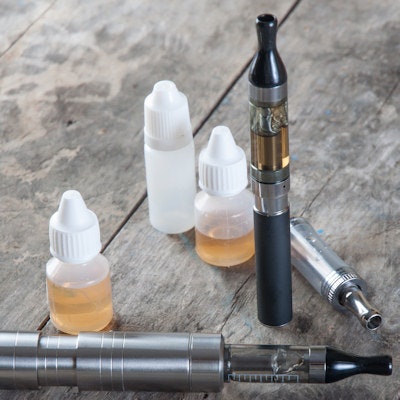
Another warning about the potentially harmful effects of electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes) has been issued. A new poster to be presented at an upcoming European conference details the health effects of e-cigarette use, and the authors urge more research in this area.
They explain how an e-cigarette device works and describe some of the potential healthcare consequences in an e-poster from the European Society of Thoracic Imaging meeting in Paris. The meeting begins in Paris on May 9, but the e-posters are available in advance.
"Vaping may not be as safe as we assume," noted Inneke Willekens, PhD, from the department of radiology at University Hospital Brussels (UZ Brussel), and Johan de Mey, PhD, head of radiology at UZ Brussel. "As vaping is increasing in popularity, there is a need for further investigation of the health effects of electronic cigarettes."
E-cigarettes are devices that produce an aerosol by heating a liquid that contains a solvent (vegetable glycerin, propylene glycol, or a mixture), flavorings, and nicotine.
In vaping, the evaporation of the liquid at the heating element is followed by rapid cooling to form an aerosol. Epidemiologic data indicate that minors are increasingly using e-cigarettes due to the robust marketing and advertising campaigns of manufacturers, according to Willekens and de Mey.
Hazards of vaping
There are risks to using these devices, the poster authors noted.
“Vaping may not be as safe as we assume.”
"Two potential hazards related to e-cigarettes are acute toxic effects caused by accidental or intentional ingestion of e-cigarette liquids and physical injury caused by the e-cigarette," they stated. "E-cigarettes both contain and emit a number of potentially toxic substances. The two primary ingredients found in e-cigarettes (propylene glycol and vegetable glycerin) are likely to expose users to a high level of toxins, and the more ingredients the user is inhaling, the greater the toxicity."
E-cigarettes produce a number of dangerous chemicals, including acetaldehyde and formaldehyde. Aldehydes in cigarette smoke impair mitochondrial function and reduce ciliary beat frequency, leading to diminished mucociliary clearance, the authors continued. The inhalation of cinnamaldehyde may increase the risk of respiratory infections in e-cigarette users.
E-cigarettes also contain acrolein, a herbicide primarily used to kill weeds, which contributes to the morbidity and mortality associated with acute lung injury and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and possibly asthma and lung cancer. Another popular flavoring, diacetyl, has been associated with the development of bronchiolitis obliterans, or "popcorn lung," when inhaled during manufacturing processes.
Oral healthcare
A 2018 report from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine noted that both human and in vitro studies suggest that e-cigarette aerosols can cause harm to oral health by inducing gingival inflammation in the oral cavity.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported in November 2018 that the use of e-cigarettes by middle and high school students may be an epidemic and that more than 20% of high school students report using e-cigarettes on a regular basis in 2018.
The FDA announced new guidelines in November 2018 for the sale of e-cigarettes and their flavor delivering systems, known as pods, in U.S. stores.
A version of this article first appeared on AuntMinnieEurope.com.