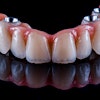
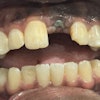
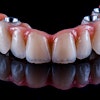
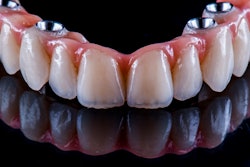
Robotic systems can offer enhanced precision and flexibility in dental implant planning, leading to improved long-term success rates for these prosthetics, according to a review article that was published in the International Journal of Oral Science.
However, the potential of robotic systems in dentistry faces challenges, including high equipment costs and the need for trained specialists, which may limit its adoption, the authors wrote.
"With the continuous improvement of technology and reduction of costs, implant robotics are gradually becoming available for commercial use," wrote the authors, led by Chen Liu of the State Key Laboratory of Oral and Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration in China (Int J Oral Sci, April, 8, 2024, Vol. 16:1, pp. 1-13).
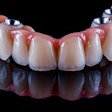
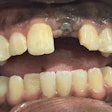
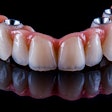
Implantology is the favored treatment for patients with partial or complete edentulous arches, aiming for both aesthetic and functional success. Proper prosthetically driven implant placement is essential to prevent complications like excessive lateral forces, misalignment, food entrapment, bone loss, and peri-implantitis, they wrote.
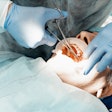
Robotic-assisted implant surgery can offer precise implant placement and enables surgeons to avoid risky tool movements during the procedure. Additionally, automatic calibration, registration, and drilling with robotic systems decrease human error compared to manual methods. This enhances surgical accuracy, safety, success rates, and efficiency while minimizing patient trauma, they added.
However, there are challenges related to dental implant robotic systems, including the need for simplification of surgical procedures and improved flexibility. While robot-assisted surgery enhances accuracy and treatment quality, it involves complex registration and calibration processes, prolonging surgery time and potentially introducing errors. Also, surgeons require extra training to effectively use these systems, they wrote.
Furthermore, the current lack of flexibility in robotic arms limits their usability in posterior sections with limited space, and marker systems may obstruct surgical maneuverability. There's a need for further research and development to address these issues, including the development of multifunctional robotic systems for various dental treatments, the authors wrote.
"By leveraging machine learning and artificial intelligence technologies, more precise diagnostic and treatment options, intelligent medical decision support systems, and flexible and precise surgical procedures will be provided for future clinical practice," they concluded.