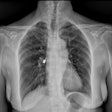
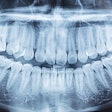
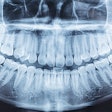
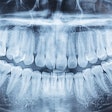
Panoramic x-rays can be used by dental practitioners to help in the early detection of strokes, according to a study by researchers from the University of Bonn (Clinical Oral Investigations, April 30, 2010).
Cerebrovascular accidents are responsible for killing or disabling more than half a million Americans every year and are the third leading cause of death in the U.S., the researchers noted. In Germany, stroke is the fourth leading cause of death, with 182 cases per 100,000 inhabitants reported annually.
Recognizing the need to find a cost-effective means of decreasing stroke mortality and morbidity, the researchers set out to demonstrate the potential of panoramic radiographs used in everyday clinical dental practice to meet this need -- specifically, radiopaque findings in the carotid region.
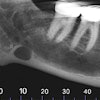
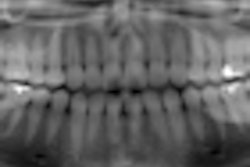
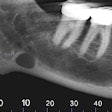
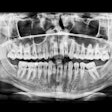
The study included panoramic dental radiographs of 2,557 patients age 30 years or older (59% women, 41% men). The radiographs were evaluated for signs compatible with carotid arterial calcifications appearing as a radiopaque nodular mass adjacent to the cervical vertebrae at or below the intervertebral space C3-4.
Of these radiographs, 4.8% (64.8% of the women, 35.2% of the men) showed radiopaque findings compatible with atherosclerotic lesions. The study results show that about 5% of the patients showed radiological findings compatible with carotid arterial calcifications, the researchers noted.
"Some of these patients at risk for a cerebrovascular accident may be identified in the dentist's office by appropriate review of the panoramic dental radiograph," they wrote. "The suspicion of carotid artery calcifications demands an impetuous referral to an appropriate practitioner who can assist in the control of risk factors and if necessary arrange surgical removal of the carotid arterial plaque."
Dental practitioners who are aware of this problem could help in early stroke detection and prevention, they concluded.
Copyright © 2010 DrBicuspid.com