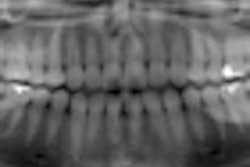
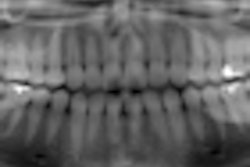
A panoramic imaging system that uses a sophisticated digital signal processing technique based on tomosynthesis continues to show promise as a high-resolution, low-dose alternative to intraoral radiography, according to research presented at the recent 2010 Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery conference in Geneva.
Working with a PanoACT-1000 (Axion) equipped with a high-speed data acquisition device utilizing a solid-state detector, researchers from Showa University obtained images from 10 patients. Each panoramic image was divided into 14 parts using the system's region of interest program to create a series similar to a full-mouth intraoral survey. Each image was then manipulated to obtain optimal image quality of the teeth and surrounding structures.
The image quality was evaluated by five oral radiologists who considered:
- Visibility of the contour of the root
- Root canal space
- Periodontal membrane space
- Lamina dura
- Alveolar bone
- Proximal enamel
- Floor of the maxillary sinus
They used the following rating system:
- Not seen
- Difficult to see
- Can be seen
- Good visualization
- Excellent visualization
The visibility of the anatomical structures was scored above a 3 by all observers.
"The new panoramic system has made it possible to reconstruct any selected arbitrary plane for a specific dental arch shape and to incline this image plane from the original data acquisitions," the researchers reported. "Optimum-quality panoramic images, regardless of variations in patient positioning, can also be obtained."
Due to high sensitivity of the cadmium telluride detector, the patient dose was reduced by more than 25% compared to a conventional panoramic system, they added.
"This panoramic system could be an alternative to intraoral radiography and thereby reducing considerable radiation dose to patients," they concluded.
Copyright © 2010 DrBicuspid.com