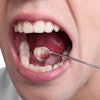
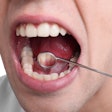
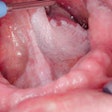
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has awarded a $1.1 million grant for research on oropharynx cancer related to human papillomavirus (HPV).
Administered by the Office of Orphan Products Development, the three-year grant will support an ongoing phase II trial by researchers from Baylor College of Medicine (BCM) and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. The study will test the efficacy of axalimogene filolisbac (ADXS-HPV) immunotherapy for patients with HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer.
"We hope to improve outcomes in HPV-associated head and neck cancer by exploring axalimogene filolisbac in this indication, where existing treatment options are associated with risk of long-term morbidity," stated lead researcher Andre Sikora, MD, an associate professor of otolaryngology at BCM, in a press release. "If successful, this trial could pave the way for immunotherapy to become a standard treatment for HPV-associated cancers."
Axalimogene filolisbac was developed by Advaxis, a clinical-stage biotechnology company developing cancer immunotherapies. It is in clinical trials for three potential cancer indications: invasive cervical, head and neck, and anal cancers