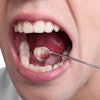
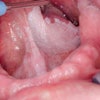
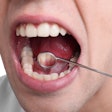
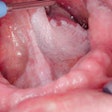
Chinese researchers have established a link between human papillomavirus (HPV) and laryngeal cancers, and estimate that it increases risk by five times, according to a study in the Journal of Infectious Diseases (November 21, 2012).
The researchers at the Institute of Pathogen Biology in Beijing systematically reviewed studies on HPV infection and laryngeal cancer that had been published up to May 15, 2012. Their meta-analysis of 55 studies found that the overall HPV prevalence in laryngeal cancer tissues was 28%.
They also found that 26.6% of laryngeal cancer patients had high-risk types of HPV only, and HPV-16 was the most common with a prevalence of 19.8%.
In addition, the meta-analysis of 12 case-control studies suggests a strong association between HPV infection and laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma with a summarized odds ratio of 5.39.
"HPV infection, especially high-risk type HPV-16, was found to be significantly associated with the risk of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma," the researchers concluded.