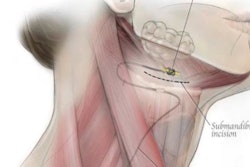
A clinical trial is under way at Henry Ford Hospital to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of the Apnex hypoglossal nerve stimulation (HGNS) system in treating obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
The Apnex system is a surgically implanted medical device that activates muscles of the upper airway to ensure that the airway remains open during sleep. While asleep, the system monitors the patient's breathing and delivers mild stimulation to the hypoglossal nerve, which controls the tongue. As the nerve is stimulated, the tongue gently moves forward to keep the airway open.
The stimulation is timed to a patient's own breathing pattern. The device automatically turns on when the patient is sleeping, and turns off when the patient is awake.
The purpose of the Apnex Clinical Study is to determine whether the Apnex system is a safe and effective treatment for OSA in patients who have not received lasting benefit from other OSA treatments. The study is being performed by sleep specialists at centers throughout the U.S., Australia, and Europe.