The U.S. Department of Defense has awarded the University at Buffalo in New York a $1.5 million grant to use toward oral cancer research.
The three-year grant will allow the university to focus on "reprogramming" a type of white blood cell called a macrophage that migrates to oral tumors and triggers inflammation. This process can suppress the body's immune response and reduce the effectiveness of cancer therapy.
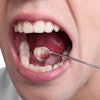
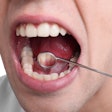
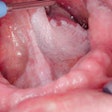
The research will be led by Dr. Keith Kirkwood, PhD, and will concentrate on oral squamous cell carcinoma. Veterans are twice as likely to develop oral cancer compared to their nonmilitary counterparts, the university noted.
"A change in behavior in the white blood cells within the tumor itself removes the 'brakes' in the system, causing more oral cancer growth," Kirkwood said in a statement released by the university. "We propose to reprogram the white blood cells to regain control of the brakes."