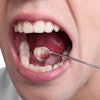
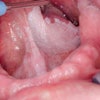
Nisin, a common food preservative, may slow or stop squamous cell head and neck cancers (HNC), a University of Michigan (U-M) study has found (Cancer Medicine, October 2, 2012).
What makes this particularly good news is that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the World Health Organization approved nisin as safe for human consumption decades ago, according to Yvonne Kapila, DDS, PhD, the study's principal investigator and a professor at the U-M School of Dentistry.
This means that obtaining FDA approval to test nisin's suggested cancer-fighting properties on patients in a clinical setting won't take as long as a new therapy that hasn't been tried yet on people, she said.
Antibacterial agents alter cell properties in bacteria to render it harmless. However, it's only recently that scientists began looking to antibacterial agents such as nisin to see if they altered properties in other types of cells, such as cancer or tumor cells.
"The poor five-year survival rates for oral cancer underscore the need to find new therapies for oral cancer," Dr. Kapila said. "The use of small antibacterial agents, like nisin, to treat cancer is a new approach that holds great promise. Nisin is a perfect example of this potential because it has been used safely in humans for many years, and now the laboratory studies support its antitumor potential."
The U-M study, which looked at the use of antimicrobials to fight cancerous tumors, suggests nisin, in part, slows cell proliferation or causes cell death through the activation of a protein called CHAC1 in cancer cells, a protein known to influence cell death.
The study is the first to show CHAC1's new role in promoting cancer cell death under nisin treatment. The findings also suggest that nisin may work by creating pores in the cancer cell membranes that allow an influx of calcium. It's unclear what role calcium plays in nisin-triggered cell death, but it's well known that calcium is a key regulator in cell death and survival.
Additionally, the findings suggest that nisin slows or stops tumor growth by interrupting the cell cycle in "bad" cells but not the good cells; thus nisin stops cancer cell proliferation but doesn't hurt good cells.