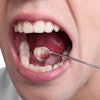
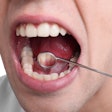
The OralCDx (Oral Cancer Prevention International) brush test demonstrated high sensitivity and specificity values in diagnosing and monitoring oral leukoplakia, according to a study in Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Surgery (July 15, 2011).
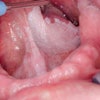
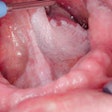
Researchers from the University of Santiago de Compostela in Spain took OralCDx samples from 24 patients (12 men, 12 women; average age 62 years) who visited the university's oral medicine, oral surgery, and implantology department between February 2009 and May 2010. The patients all presented with clinical and histological lesions consistent with oral leukoplakia, the researchers noted.
They evaluated the relationship between the keratinization degree of the lesions and cell representation, with the diagnosis obtained through OralCDx and biopsies, and sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV).
They found that the Kappa coefficient relating keratinization of lesions and cell representation was 0.33. In addition, the OralCDx biopsy diagnostic rate reached a Kappa value of 0.66, recording 72.7% sensitivity and 92.3% specificity. The PPV was 88.8%, while the NPV reached 80%.
Cytology sampling with the OralCDx showed high sensitivity and specificity values, making it a good tool for monitoring oral leukoplakia, the researchers concluded.
However, "nowadays the most reliable method that allows us to confirm the exact diagnosis of the lesions and their anatomical and pathological characteristics still is conventional biopsy using a surgical scalpel," they added.